1 GHz = 1000 MHz
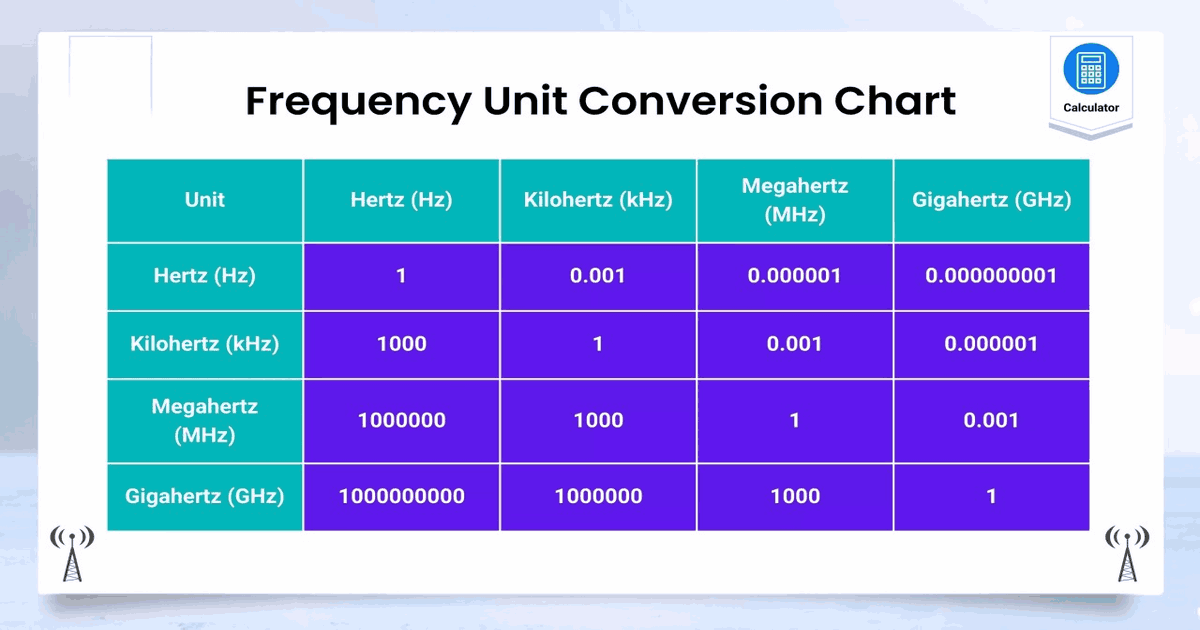
Hertz (Hz)
Hertz is the base unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI). It represents one cycle or oscillation per second. For example, if a wave completes one full cycle in one second, its frequency is 1 Hz.
Gigahertz (GHz)
Gigahertz is a multiple of hertz, specifically one billion hertz. It’s used to express frequencies that are much higher than the typical frequencies encountered in everyday situations. For example, a computer’s processor speed might be measured in gigahertz. If a processor operates at 1 GHz, it completes one billion cycles per second.
Gigahertz to Hertz Conversion Table
| Gigahertz (GHz) | Hertz (Hz) |
|---|---|
| 0.001 GHz | 1,000,000 Hz |
| 0.002 GHz | 2,000,000 Hz |
| 0.003 GHz | 3,000,000 Hz |
| 0.004 GHz | 4,000,000 Hz |
| 0.005 GHz | 5,000,000 Hz |
| 0.006 GHz | 6,000,000 Hz |
| 0.007 GHz | 7,000,000 Hz |
| 0.008 GHz | 8,000,000 Hz |
| 0.009 GHz | 9,000,000 Hz |
| 0.01 GHz | 10,000,000 Hz |
| 0.02 GHz | 20,000,000 Hz |
| 0.03 GHz | 30,000,000 Hz |
| 0.04 GHz | 40,000,000 Hz |
| 0.05 GHz | 50,000,000 Hz |
| 0.06 GHz | 60,000,000 Hz |
| 0.07 GHz | 70,000,000 Hz |
| 0.08 GHz | 80,000,000 Hz |
| 0.09 GHz | 90,000,000 Hz |
| 0.1 GHz | 100,000,000 Hz |
| 0.2 GHz | 200,000,000 Hz |
| 0.3 GHz | 300,000,000 Hz |
| 0.4 GHz | 400,000,000 Hz |
| 0.5 GHz | 500,000,000 Hz |
| 0.6 GHz | 600,000,000 Hz |
| 0.7 GHz | 700,000,000 Hz |
| 0.8 GHz | 800,000,000 Hz |
| 0.9 GHz | 900,000,000 Hz |
| 1 GHz | 1,000,000,000 Hz |
| 2 GHz | 2,000,000,000 Hz |
| 3 GHz | 3,000,000,000 Hz |
How to Convert Gigahertz to Hertz ?
1 GHz = 1000000000 Hz
1 Hz = 1.0E-9 GHz
Example: convert 20 GHz to Hz:
20 GHz = 20 × 1000000000 Hz = 20000000000 Hz
Frequency Asked Questions :
1. What is the relationship between gigahertz and hertz?
- Gigahertz (GHz) and hertz (Hz) are both units of frequency. 1 gigahertz is equal to 1,000,000,000 hertz.
2. How do I convert gigahertz to hertz?
- To convert gigahertz to hertz, multiply the number of gigahertz by 1,000,000,000. For example, to convert 2 GHz to Hz: 2 GHz * 1,000,000,000 = 2,000,000,000 Hz.
3. Why is it necessary to convert between gigahertz and hertz?
- While gigahertz is commonly used to express frequencies in modern technology, hertz is the base unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI). Converting between the two units may be necessary for certain calculations or when comparing frequencies across different systems.
4. In what contexts are gigahertz and hertz used?
- Gigahertz is often used to describe the clock speed of computer processors, the frequency of electromagnetic waves in telecommunications, and other high-frequency phenomena. Hertz, being the SI unit, is used across various scientific disciplines to measure any type of periodic motion or vibration.
5. What are some examples of frequencies in gigahertz and hertz?
- Common examples of frequencies in gigahertz include Wi-Fi signals (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), microwave ovens (2.45 GHz), and some radio frequency identification (RFID) systems. Hertz is used for a wide range of frequencies, from extremely low frequencies such as those in power grids (50-60 Hz) to extremely high frequencies such as gamma rays (>10^19 Hz).